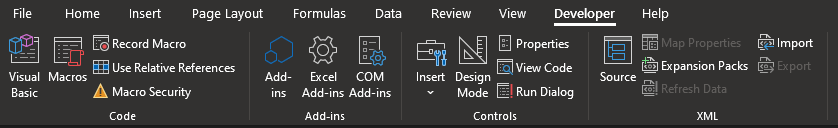
Visual Basic Editor
The Visual Basic Editor (VBE) is the built-in Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for coding in VBA. The Visual Basic Editor provides a place to write, run, debug, and store VBA code. The Visual Basic Editor is embedded into applications that support VBA and does not need to be separately downloaded or installed.
Accessing the VBE
To access the Visual Basic Editor in Microsoft Office applications use the Alt + F11 keyboard shortcut. In most Office applications the Developer Tab can be added to the ribbon and used to access the Visual Basic Editor and other developer features. To add the Developer Tab to the ribbon check the Developer checkbox in File → Options → Customize Ribbon.
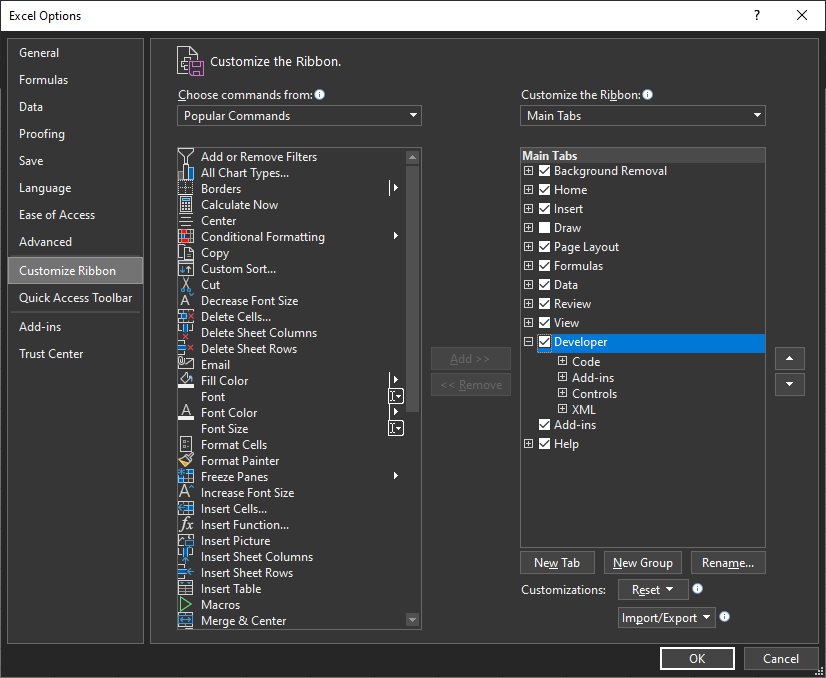
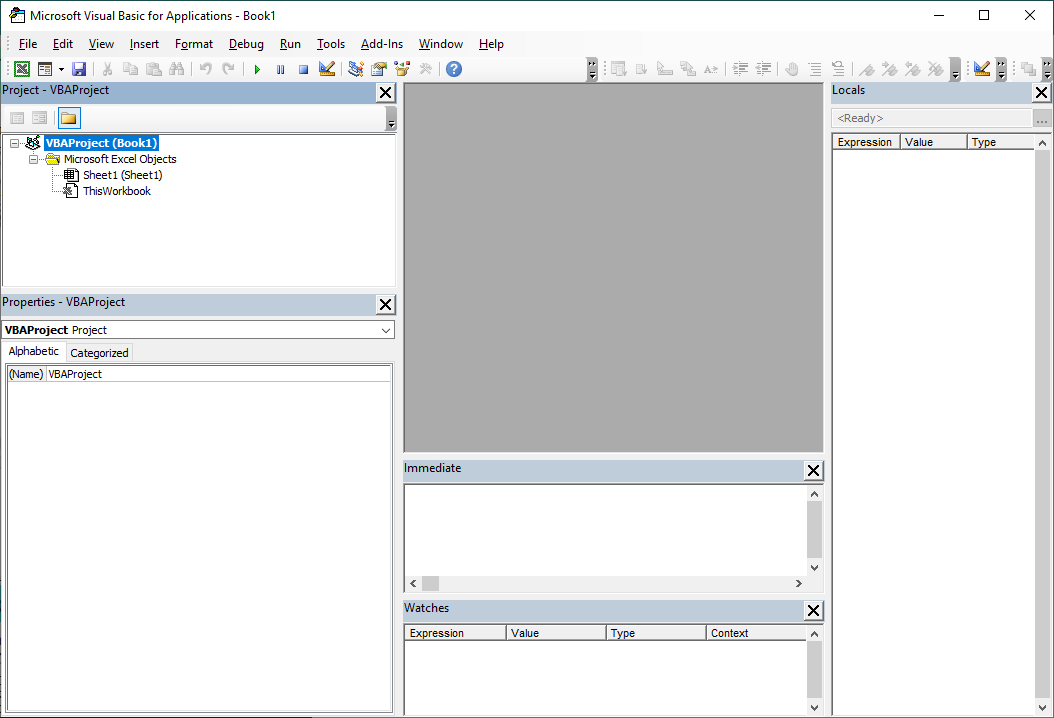
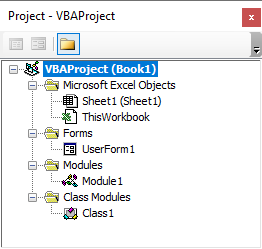
Project Explorer
The Project Explorer shows open VBA projects within the application and the objects associated with the projects. The Project Explorer is used to access and navigate VBA projects; insert, import, export, and remove code modules; and access the properties of objects. Double-click or right-click on objects to access their code modules or access their properties.
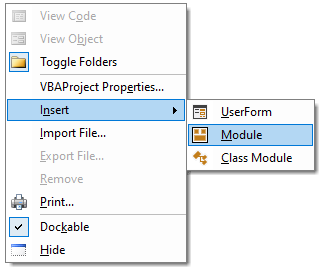
Modules
VBA code is stored inside Modules. There are Standard modules, Class modules, UserForm modules, and modules associated with application-specific objects like Excel Worksheets. UserForm modules and modules associated with application-specific objects are special types of class modules that are attached to an object.
Standard modules, Class modules, and UserForms can be inserted or imported by right-clicking in the Project Explorer within a VBA project. The code modules for application-specific objects like Worksheets and Workbooks are added automatically to the VBA project when these objects are created.
Code Windows
Code Windows are where code is written in VBA. Every code module has its own dedicated code window that is specifically for that module.
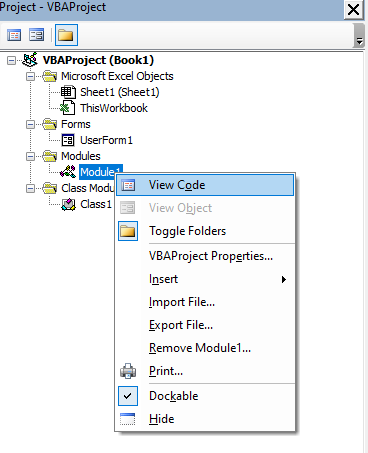
To open the code window for a module, double-click the code module or right-click the code module and select View Code in the Project Explorer.
Object Box
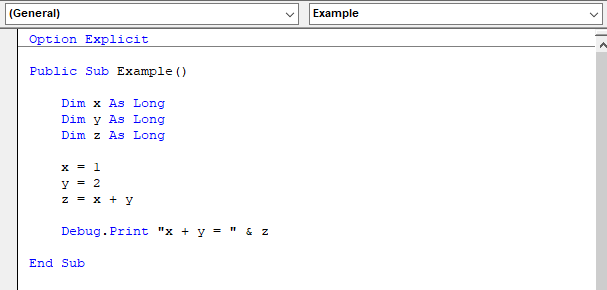
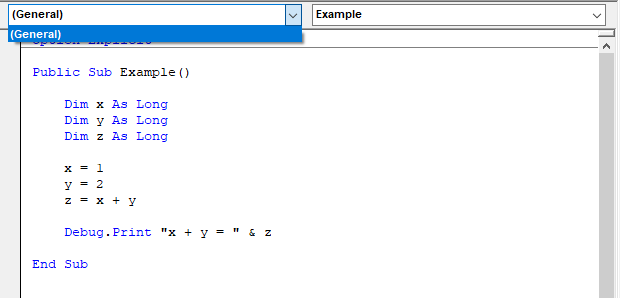
The Object Box is used to select a codeable object associated with the current code module. General is the default selection and denotes that no specific object is selected.
Procedure Box
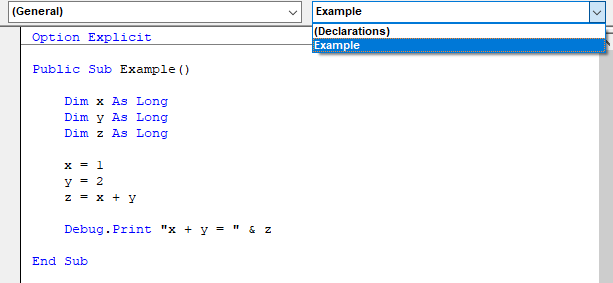
The Procedure Box is used to select the procedures available to the codeable object selected by the Object box. When General is selected the drop-down will contain all procedures declared in the module.
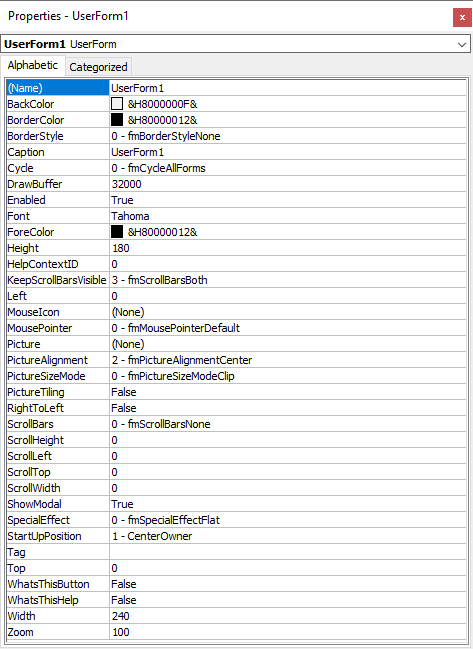
Properties Window
The Properties Window allows the user to set the properties of a VBA project or items within a VBA project. To open the properties window use the View menu on the toolbar in the Visual Basic Editor and select Properties Window or press F4. Select items within a VBA project to show the properties for that item.
Watch Window
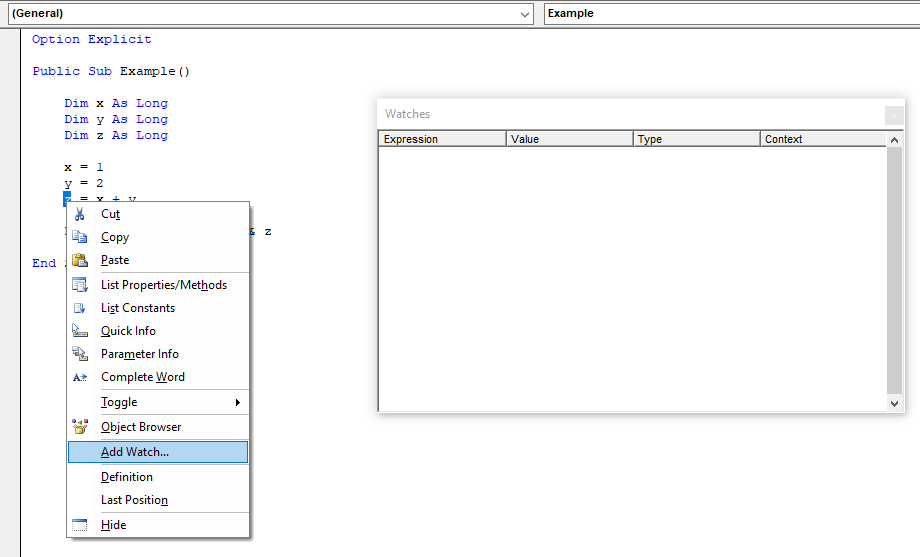
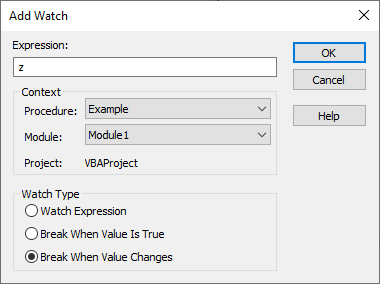
The Watch Window is used to view how expressions evaluate during a program's execution and to pause execution when certain conditions are reached. To add a watch, highlight an expression, right-click the expression, and select Add Watch. Alternatively, right-click the Watch Window, select Add Watch, and type the expression. To access the Watch Window navigate to View → Watch Window.
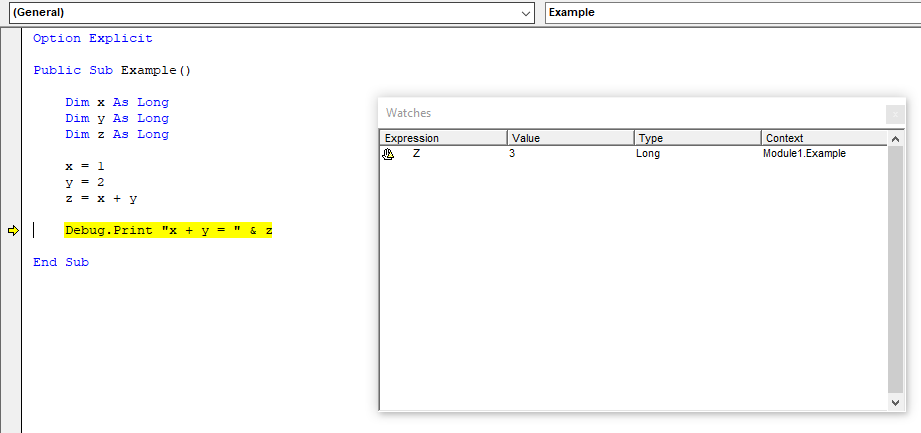
Locals Window
The Locals Window is used to view the states of variables during the execution of a program. To access the Locals Window navigate to View → Locals Window.
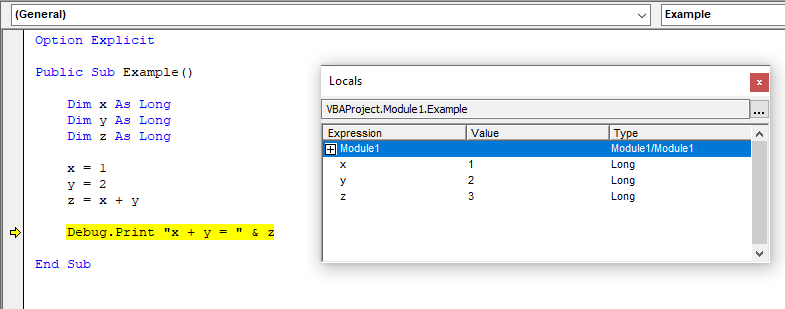
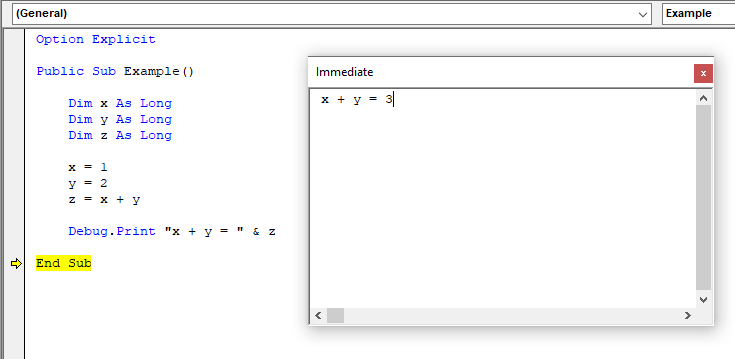
Immediate Window
The Immediate Window is used to print data from a program, call procedures, set values and properties, call methods on objects, and query the result of an expression. To access the Immediate Window use the Ctrl + G keyboard shortcut or navigate to View → Immediate Window.
Printing
Using Debug.Print will output text to the Immediate Window.
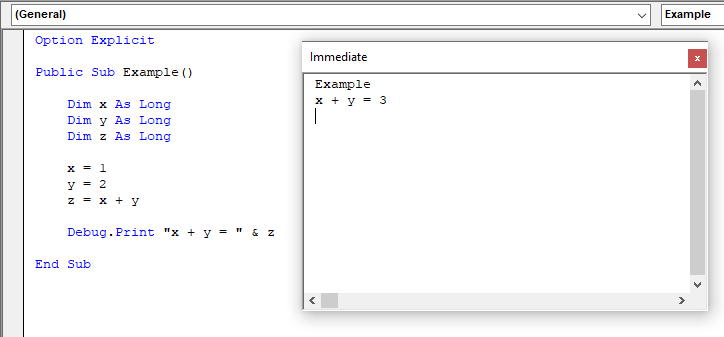
Calling Procedures
To call a procedure simply type the procedure name in the Immediate Window, pass arguments if there are any, and press Enter.
Setting Values
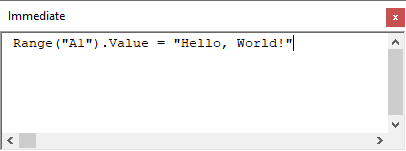
Values of variables and properties of objects can be set or queried during the execution of a procedure using the Immediate Window.
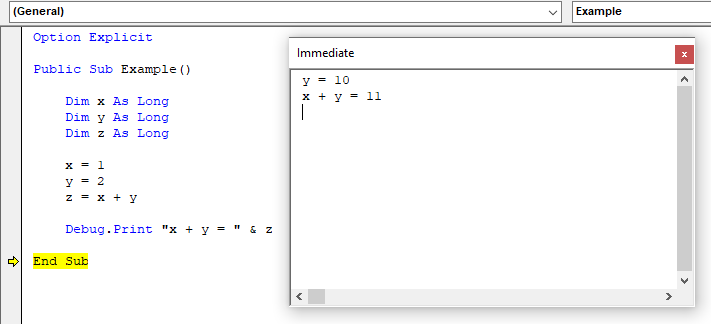
Properties of objects like Worksheets in Excel can be set at any time in the Immediate Window.
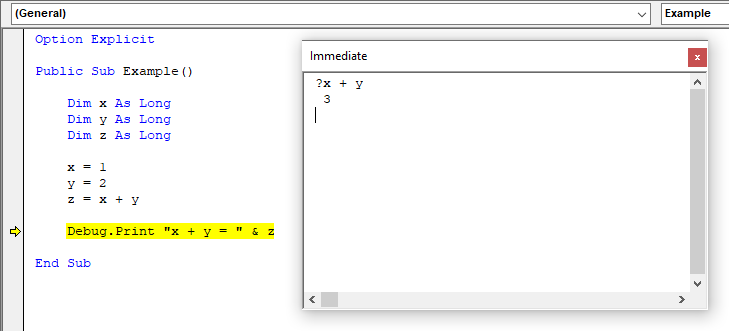
Evaluating Expressions
An expression can be evaluated in the Immediate Window by using a question mark ("?") followed by an expression. Expressions can also be tested while a program's execution is paused, giving access to a program's current state.
Object Browser
The Object Browser is used to view the members of VBA code libraries. Specific members can be searched and the browser can be filtered by library. Selecting an object will show its members. Setting a reference to a library will cause it to appear in the Object Browser. To access the Object Browser press F2, click the Object Browser icon on the Standard Toolbar, or navigate to View → Object Browser.
Toolbars
There are several important toolbars that make coding, debugging, and form design in VBA much easier. These are: Debug, Edit, Standard, and UserForm. To access these toolbars navigate to View → Toolbars. Toolbars can be edited and custom toolbars can be created by selecting View → Toolbars → Customize.

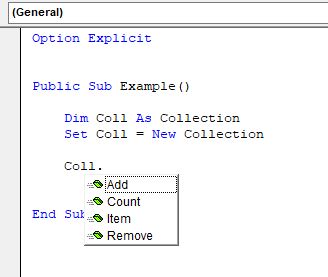
Intellisense
Intellisense and auto-code completion assist in typing code by suggesting or completing code. The intellisense drop-down will show up automatically underneath the cursor when the dot (".") operator is used to access an object's members as long as the Visual Basic Editor can resolve the reference to an early-bound object. The intellisense drop-down can also be invoked using the Ctrl + j shortcut. The Ctrl + space shortcut will complete code if there is only one possible way to complete the code or it will display the intellisense drop-down if there is more than one way complete the code.
| Shortcut | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Ctrl + Space | Complete Word |
| Ctrl + j | Show Intellisense |
Bookmarks
Bookmarks are used to jump to different positions in code in any module.
Bookmarks are indicated by a blue square in the left margin.
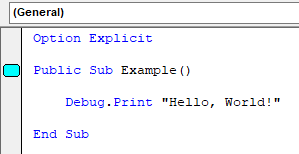
Bookmarks can be set, removed, or navigated to using the Edit toolbar which can be enabled from View → Toolbars.
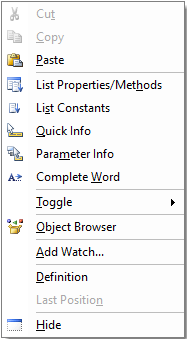
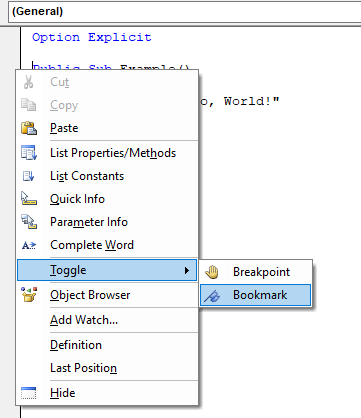
The right-click menu can be used to toggle bookmarks.
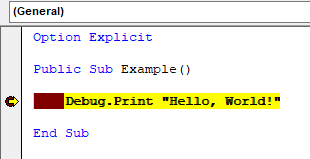
Breakpoints
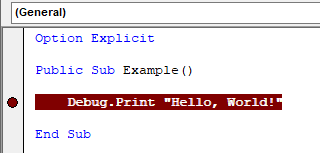
Breakpoints can be set on specific lines of code which will halt the execution of the program before executing those lines. Breakpoints can be set by clicking in the margin next to a line of code or right-clicking and selecting Toggle → Breakpoint.
Options
To change options in the Visual Basic Editor navigate to Tools → Options. The Options dialog has 4 tabs: Editor, Editor Format, General, and Docking.
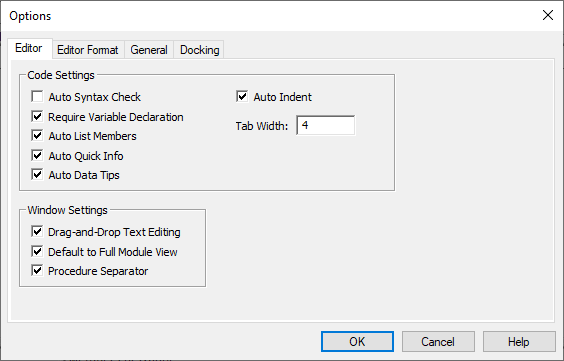
Editor
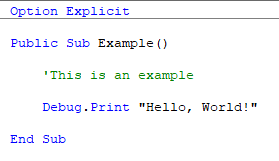
The Editor tab has options to control the behavior of the Visual Basic Editor. It is common to uncheck Auto Syntax Check to remove pop-ups for syntax errors and to check Require Variable Declaration to add Option Explicit to the top of new modules.
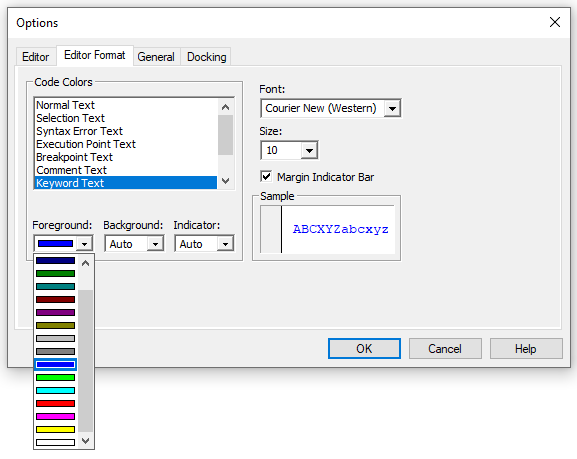
Editor Format
The Editor Format tab has options to control the appearance of the Visual Basic Editor. This is a matter of personal preference but in general the default appearance is sufficiently optimal and intuitive. One change that may improve the default appearance is to change the color of Keyword Text to a brighter blue because the default can be difficult to see at times. Blue/Green is nicely visible as well and less intense to look at but it may be necessary to change the Comment text color as well to purple.

General
The General tab has miscellaneous options for the Visual Basic Editor. Changing Error Trapping to "Break on All Errors" can be useful for debugging but should generally be left on "Break on Unhandled Errors" for error handling code to work. "Break in Class Module" is useful for debugging when working with user-defined classes.
Docking
The Docking tab is used to allow or prohibit the docking of various windows in the Visual Basic Editor.
Close the VBE before Running Code
If the Visual Basic Editor is open while a program is executing, the status bar in the VBE will continuously update which significantly reduces performance and speed. When running resource intensive code it is wise or may even be necessary to close the Visual Basic Editor before running the procedure.



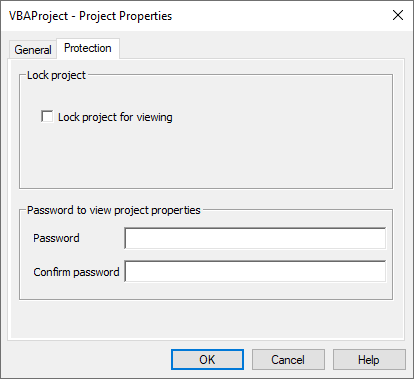
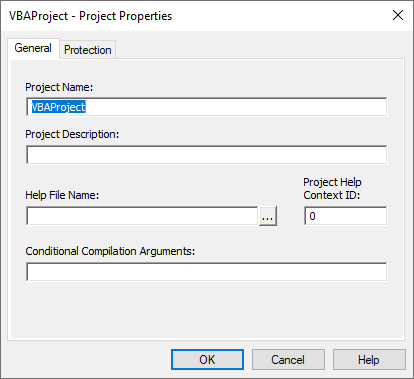
VBA Project Properties
The VBA Project Properties dialog box can be accessed by right-clicking in the Project Window and selecting VBA Project Properties.
General
The project name, project description, help file, help file context ID, and Conditional Compiler Constants can be set in the General tab of the VBA project Properties Window.
Protection
Password protect a VBA project by checking "Lock project for viewing" and providing a password in the Protection tab.