VBA Libraries
Libraries are used to access functionality outside of what VBA can do on its own. There are a number of VBA libraries provided by the Windows operating system, Office applications, and other software installed by the user. Libraries are often used to control a specific application or access classes which serve specific purposes. Libraries can be used to write VBA programs that utilize multiple applications, access the user's file system, manipulate text files and databases, get information from the internet, and more.
Set Library References
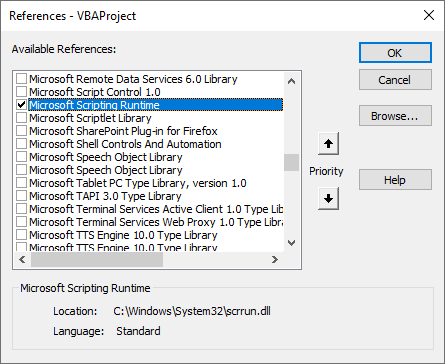
Setting a reference to a library allows a VBA project to access the members of the library directly. Setting a reference allows the VBA compiler and the Visual Basic Editor to see the members of a library. Setting a reference allows for early-binding of object variables, enables intellisense, and makes the library visible in the Object Browser. To set a reference to a library navigate to Tools → References in the Visual Basic Editor and check the library and click Ok. Members of a library can be accessed without a reference by using late-binding (declaring an object variable with the generic Object type and using the CreateObject function with the class's ProgID). Early-binding vs late-binding is discussed in the Objects section.
Fully Qualified Identifiers
When using libraries, be sure to use the fully qualified names for classes, variables, and procedures to avoid naming collisions. There are times when a library contains an identifier that is the same as another identifier in VBA or another library. If the name is not fully qualified, VBA will not know which identifier is being referred to and errors can occur. To fully qualify an identifier's name include the library of origin.
Public Sub Example()
'References set to Excel object library and Word object library
Dim ExcelApp As Excel.Application
Dim WordApp As Word.Application
Set ExcelApp = Excel.Application
Set WordApp = Word.Application
End Sub
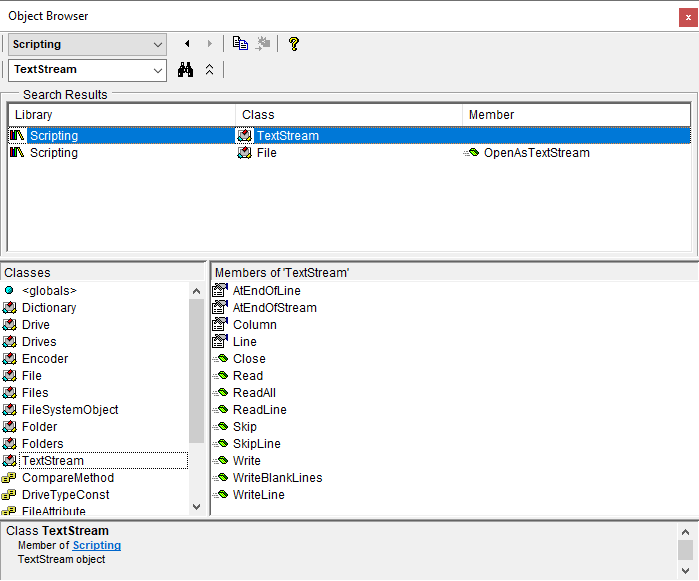
Exploring Libraries
To explore the contents of a library in detail set a reference to the library and use the Object Browser to view the library's members.
Search and Browse Specific Libraries
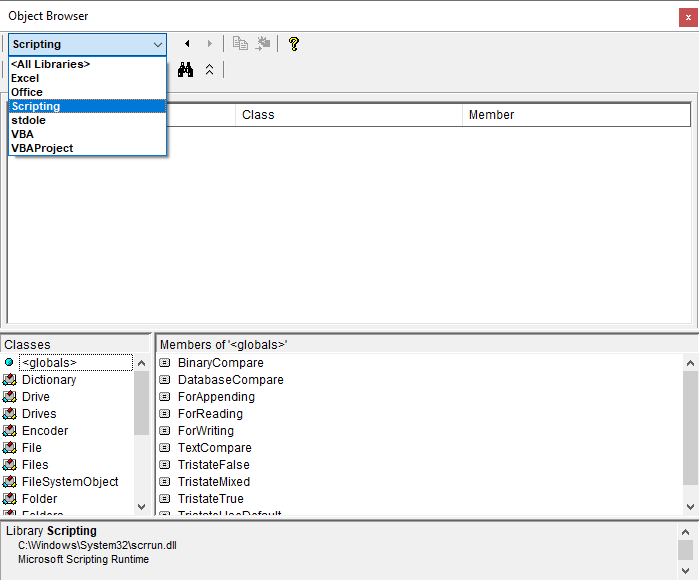
Specific libraries can be browsed and searched by selecting the library from the library drop-down.
View Class Members
Select an item in the Classes section and view its members in the Members section.
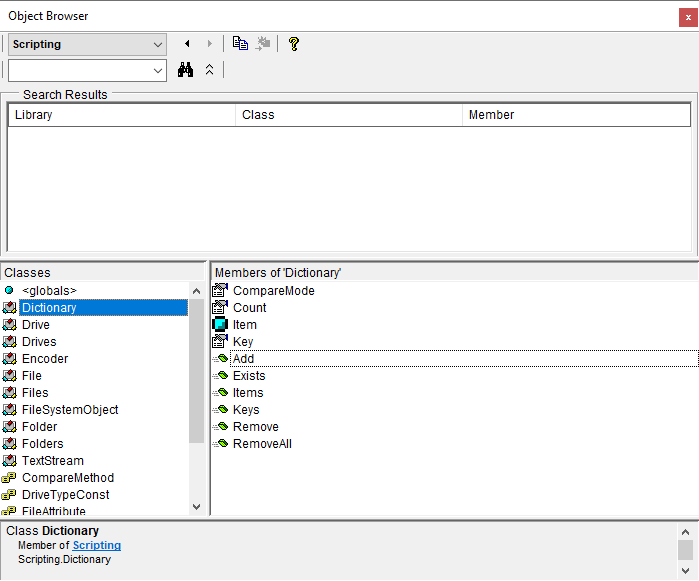
Search
Use the search bar to search for specific text related to a class or member. Select an item in the Search Results to view its members in the members section.
Important Libraries
There are a number of important libraries which are very commonly used and are often necessary for accomplishing tasks in VBA.
| Name: |
Scripting |
| Description: |
Microsoft Scripting Runtime |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\scrrun.dll |
| GUID: |
{420B2830-E718-11CF-893D-00A0C9054228} |
| Use Cases: |
File System, Text Files, Dictionary Class |
| Name: |
ADODB |
| Description: |
Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 6.1 Library |
| FullPath: |
C:\Program Files\Common Files\System\ado\msado15.dll |
| GUID: |
{B691E011-1797-432E-907A-4D8C69339129} |
| Use Cases: |
Databases, Text Files |
| Name: |
MSHTML |
| Description: |
Microsoft HTML Object Library |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\mshtml.tlb |
| GUID: |
{3050F1C5-98B5-11CF-BB82-00AA00BDCE0B} |
| Use Cases: |
HTML, DOM |
| Name: |
SHDocVw |
| Description: |
Microsoft Internet Controls |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\ieframe.dll |
| GUID: |
{EAB22AC0-30C1-11CF-A7EB-0000C05BAE0B} |
| Use Cases: |
IE Automation |
| Name: |
WinHttp |
| Description: |
Microsoft WinHTTP Services, version 5.1 |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\system32\winhttpcom.dll |
| GUID: |
{662901FC-6951-4854-9EB2-D9A2570F2B2E} |
| Use Cases: |
HTTP Requests |
| Name: |
MSXML2 |
| Description: |
Microsoft XML, v3.0 | v6.0 |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\msxml3.dll | C:\Windows\System32\msxml6.dll |
| GUID: |
{F5078F18-C551-11D3-89B9-0000F81FE221} |
| Use Cases: |
XML, HTTP Requests |
| Name: |
Shell32 |
| Description: |
Microsoft Shell Controls And Automation |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\SysWOW64\shell32.dll |
| GUID: |
{50A7E9B0-70EF-11D1-B75A-00A0C90564FE} |
| Use Cases: |
Shell, Zip Files, File System |
| Name: |
IWshRuntimeLibrary |
| Description: |
Windows Script Host Object Model |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\wshom.ocx |
| GUID: |
{F935DC20-1CF0-11D0-ADB9-00C04FD58A0B} |
| Use Cases: |
Shell, Shortcuts, File System, Network, Registry |
| Name: |
VBScript_RegExp_55 |
| Description: |
Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5 |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\System32\vbscript.dll\3 |
| GUID: |
{3F4DACA7-160D-11D2-A8E9-00104B365C9F} |
| Use Cases: |
Regular Expressions |
| Name: |
VBIDE |
| Description: |
Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications Extensibility 5.3 |
| FullPath: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\VBA\VBA6\VBE6EXT.OLB |
| GUID: |
{0002E157-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
| Use Cases: |
Visual Basic Editor, Project References |
| Name: |
mscorlib |
| Description: |
mscorlib.dll |
| FullPath: |
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319\mscorlib.tlb |
| GUID: |
{BED7F4EA-1A96-11D2-8F08-00A0C9A6186D} |
| Use Cases: |
ArrayList |
Microsoft Office Applications
To work with more than one Office application in a single VBA program it is helpful to set references to all Office applications being used.
| Name: |
Access |
| Description: |
Microsoft Access 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\MSACC.OLB |
| GUID: |
{4AFFC9A0-5F99-101B-AF4E-00AA003F0F07} |
| Name: |
Excel |
| Description: |
Microsoft Excel 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\EXCEL.EXE |
| GUID: |
{00020813-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
| Name: |
Outlook |
| Description: |
Microsoft Outlook 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\MSOUTL.OLB |
| GUID: |
{00062FFF-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
| Name: |
PowerPoint |
| Description: |
Microsoft PowerPoint 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\MSPPT.OLB |
| GUID: |
{91493440-5A91-11CF-8700-00AA0060263B} |
| Name: |
Publisher |
| Description: |
Microsoft Publisher 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\MSPUB.TLB |
| GUID: |
{0002123C-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
| Name: |
Word |
| Description: |
Microsoft Word 16.0 Object Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\MSWORD.OLB |
| GUID: |
{00020905-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
| Name: |
Visio |
| Description: |
Microsoft Visio 16.0 Type Library |
| FullPath |
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\root\Office16\VISLIB.DLL |
| GUID: |
{00021A98-0000-0000-C000-000000000046} |
Adobe Acrobat
The Adobe Acrobat Library can be used to automate the Adobe Acrobat application and work with PDF files. Adobe Acrobat must be purchased from Adobe and installed in order for the VBA libraries to be available.
| Name: |
Acrobat |
| Description: |
Adobe Acrobat 10.0 Type Library |
| FullPath: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Adobe\Acrobat 2017\Acrobat\acrobat.tlb |
| GUID: |
{E64169B3-3592-47D2-816E-602C5C13F328} |
| Name: |
AFORMAUTLib |
| Description: |
AFormAut 1.0 Type Library |
| FullPath: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Adobe\Acrobat Reader DC\Reader\plug_ins\AcroForm.api |
| GUID: |
{7CD06992-50AA-11D1-B8F0-00A0C9259304} |
Micro Focus Reflection
The Micro Focus Reflection libraries can be used to automate tasks in the Micro Focus Reflection application. Micro Focus Reflection Desktop 16.1 must be purchased and installed in order for the libraries to be available.
| Name: |
Attachmate_Reflection_Objects |
| Description: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Micro Focus\Reflection\Attachmate.Reflection.Objects.tlb |
| GUID: |
{6857A7F4-4CDE-43F2-A7B1-CB18BA8AA35F} |
| Name: |
Attachmate_Reflection_Objects_Emulation_IbmHosts |
| Description: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Micro Focus\Reflection\Attachmate.Reflection.Objects.Emulation.IbmHosts.tlb |
| GUID: |
{0D5D17DF-B511-4BE5-9CD0-10DE1385229D} |
| Name: |
Attachmate_Reflection_Objects_Emulation_OpenSystems |
| Description: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Micro Focus\Reflection\Attachmate.Reflection.Objects.Emulation.OpenSystems.tlb |
| GUID: |
{3BA4C5BF-F24A-4BE4-8BAB-8BD78C2FABDE} |
| Name: |
Attachmate_Reflection_Objects_Framework |
| Description: |
C:\Program Files (x86)\Micro Focus\Reflection\Attachmate.Reflection.Objects.Framework.tlb |
| GUID: |
{88EC0C50-0C86-4679-B27D-63B2FCF1C6F4} |
Programmatically Work With Project References
To programmatically work with project references use the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications Extensibility 5.3 Library (VBIDE).
'In Immediate Window:
?SetProjectReferenceByFilePath("C:\Windows\System32\scrrun.dll")
PrintProjectReferences ThisWorkbook.VBProject
Option Explicit
Public Sub SetProjectReferenceByFilePath(FilePath As String)
'Sets Project Reference
Dim VBProj As Object 'VBIDE.VBProject
Dim Refs As Object 'VBIDE.References
Dim Ref As Object 'VBIDE.Reference
Dim RefFound As Boolean
Set VBProj = ThisWorkbook.VBProject
Set Refs = VBProj.References
For Each Ref In Refs
If Ref.FullPath = FilePath Then
RefFound = True
Exit For
End If
Next Ref
If Not RefFound Then
VBProj.References.AddFromFile FilePath
End If
End Sub
Public Sub PrintProjectReferences(Proj As Object)
'Proj As VBIDE.VBProject
Dim Ref As Object 'VBIDE.Reference
For Each Ref In Proj.References
With Ref
Debug.Print "'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''"
Debug.Print "Name: " & .Name
Debug.Print "Major Version: " & .Major
Debug.Print "Minor Version: " & .Minor
Debug.Print "Description: " & .Description
Debug.Print "FullPath: " & .FullPath
Debug.Print "GUID: " & .GUID
Debug.Print "Builtin: " & .BuiltIn
Debug.Print "Type: " & .Type
Debug.Print "'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''"
End With
Next Ref
End Sub