VBA Databases
VBA can be used to interact with various types of databases including SQL databases, Access Databases, Excel Files, and more. Use the classes in the ADODB library to connect to a database and execute queries. Queries are written using SQL, or Structured Query Language, which is a language used to work with relational database management systems (RDBMS). Connecting to a certain type of data source requires a specific connection string which can usually be found at ConnectionStrings.com. There are often options for using ODBC or OLE DB connection strings.
Connections
The ADODB Connection class is used to open a connection to a data source. The common way to use the Connection object is to instantiate a new Connection object, set the ConnectionString property, and call the Open method to open a connection to the data source. The Execute method can then be called to execute a query and return a Recordset object. Open connections should be closed after use with the Close method.
Public Sub Example()
Dim ExcelFilePath As String
ExcelFilePath = "C:\ExampleData.xlsx"
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = _
"Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & ExcelFilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
CN.Open
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Set RS = CN.Execute("SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]")
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
RS.Close
CN.Close
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
End Sub| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Attributes | Can be set to a member of the XactAttributeEnum to control transaction behavior. |
| CommandTimeout | Determines how long in seconds a command will attempt to execute before stopping and returning an error. Default is 30 seconds. |
| ConnectionString | Specifies the information used to connect to a data source. |
| ConnectionTimeout | Determines how long in seconds a connection will attempt to establish itself before stopping and returning an error. Default is 15 seconds. |
| CursorLocation | Can be set to a member of the CursorLocationEnum to determine the location of the cursor service. |
| DefaultDatabase | Specifies a default database. |
| Errors | Contains all the Error objects for the most recent error. |
| IsolationLevel | Can be set to a member of the IsolationLevelEnum to specify the level of transaction isolation. Default is adXactReadCommitted. |
| Mode | Can be set to a member of the ConnectModeEnum to control the permissions for modifying data. |
| Properties | Contains all the Property objects for the connection object. |
| Provider | Specifies the name of the provider for the connection. Can also be set in the ConnectionString property. |
| State | Indicates the state of the object as a member of the ObjectStateEnum. Can be a combination of enum members. |
| Version | Indicates the ADO version number. |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| BeginTrans | Begins a new transaction. |
| CommitTrans | Saves changes and ends current transaction. May start a new transaction. |
| RollbackTrans | Cancels changes made for the current transaction and ends the transaction. May start a new transaction. |
| Cancel | Cancels the execution of a pending asynchronous method call. |
| Close | Closes the open connection. Does not remove the Connection object from memory. |
| Execute | Executes a query or command on the data source. |
| Open | Opens a connection to a data source. |
| OpenSchema | Retrieves schema information about the data source. |
Recordsets
The ADODB Recordset class represents the set of records returns from a query to a data source. The Recordset class is used to read and manipulate records in a database. Recordsets have a cursor type which determines the behaviors and validity of certain properties and methods. Set the CursorType property of a Recordset object using a member of the CursorTypeEnum before opening the Recordset to specify the type of cursor.
Note: The RecordCount property returns -1 instead of the record count for the Forward-Only cursor and may return -1 or the record count for the Dynamic cursor.
| Cursor Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward‑Only | The cursor can only move forward through records. |
| Static | Changes made after the Recordset is opened are not visible. The cursor can be moved backward and forward. Bookmarks may or may not be supported depending on the provider. |
| Keyset | Inserted records are not visible. Deleted records are not accessible. Changes to the values of records are visible. |
| Dynamic | All changes made by all users are visible. |
Public Sub Example()
Dim ExcelFilePath As String
ExcelFilePath = "C:\ExampleData.xlsx"
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = _
"Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & ExcelFilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
CN.Open
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Set RS = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
RS.Open "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]", CN, 3 'adOpenStatic
Debug.Print RS.RecordCount
RS.MoveFirst
Do Until RS.EOF
Debug.Print RS.Fields("Header1").Value
RS.MoveNext
Loop
RS.Close
CN.Close
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
End Sub| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| AbsolutePage | Indicates the page of the current record. |
| AbsolutePosition | Indicates the ordinal position of the current record. |
| ActiveCommand | The Command object that created the Recordset. |
| ActiveConnection | The Connection object associated with the Recordset. |
| BOF | True if the current position is before the first record. Otherwise False. |
| EOF | True if the current position is after the last record. Otherwise False. |
| Bookmark | Get or set the Bookmark property to retrieve the position of the current record or set the position to a particular record. |
| CacheSize | The number of locally cached records. |
| CursorLocation | The location of the cursor service as a member of the CursorLocationEnum. |
| CursorType | The cursor type of the Recordset as a member of the CursorTypeEnum. |
| DataMember | Must be used with the DataSource property. Get or set the name of the data member that is referenced by the DataSource property. |
| DataSource | Must be used with the DataMember property. An object containing data that is represented by the Recordset. |
| EditMode | The editing status of the current record as a member of the EditModeEnum. |
| Fields | A collection of all the Field objects in the Recordset. |
| Filter | A data filter for the Recordset as a criteria string, an array of bookmarks, or a member of the FilterGroupEnum. |
| Index | The name of the index for the Recordset. |
| LockType | The type of lock placed on records during editing as a member of the LockTypeEnum. |
| MarshalOptions | Determines records that are marshalled back to server. A member of the MarshalOptionsEnum. |
| MaxRecords | The maximum number of records that a query can return to the Recordset. |
| PageCount | The number of pages in the Recordset. |
| PageSize | The number of records that make up one page of the Recordset. |
| Properties | Contains all Property objects for the Recordset object. |
| RecordCount | The number of records in the Recordset. The cursor type determines whether or not the record count can be obtained. The RecordCount property returns -1 for Forward-Only, the record count for Static and Keyset, and either -1 or the record count for Dynamic, depending on the data source. |
| Sort | A string specifying fields on which to sort and whether the sort is ascending or descending. |
| Source | The data source for the Recordset. |
| State | Indicates the state of the object as a member of the ObjectStateEnum. Can be a combination of enum members. |
| Status | The status of the current record as a member of the RecordStatusEnum. Used with batch updates and bulk edits. |
| StayInSync | Determines if the reference to child records changes when the parent row position changes in a hierarchical recordset. |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| AddNew | Creates a new record. |
| Cancel | Cancels the execution of a pending asynchronous method call. |
| CancelBatch | Cancels a pending batch update. |
| CancelUpdate | Cancels the changes made to a row of the Recordset object. |
| Clone | Creates a clone of the Recordset object. |
| Close | Closes the Recordset. |
| CompareBookmarks | Compares two bookmarks and returns a member of the CompareEnum indicating the relative difference. |
| Delete | Deletes the current record or a group of records. |
| Find | Searches the Recordset for a row matching given criteria. |
| GetRows | Returns an array of records from the Recordset. |
| GetString | Returns the Recordset as a string. |
| Move | Moves the position of the current record either by a number of records, to a bookmark, or to a record specified by a member of the BookmarkEnum. |
| MoveFirst | Moves to the first record in the Recordset. |
| MoveLast | Moves to the last record in the Recordset. |
| MoveNext | Moves to the next record in the Recordset. |
| MovePrevious | Moves to the previous record in the Recordset. |
| NextRecordset | Clears the current Recordset and returns the next Recordset. Used with multiple command statements separated by ";". |
| Open | Opens the Recordset. |
| Requery | Updates the data in the Recordset by re-executing the query. |
| Resync | Refreshes the data in the Recordset. |
| Save | Saves the Recordset to a file or Stream object. |
| Seek | Searches for a row according to criteria and changes the current position to that row. |
| Supports | Indicates if the Recordset supports a certain functionality. |
| Update | Saves changes made to the current row. |
| UpdateBatch | Writes all pending batch updates. |
Commands
The Command class represents a command to execute on a database. A Command object can be used along with the Parameter class to create prepared statements. Create Parameter objects using the CreateParameter method and add the Parameter objects to the Parameters collection property of the Command object. Question marks can be used inside a command string as placeholders for parameters which will be assigned positionally from the Parameters collection. Named parameters can also be used in the command string. An array of parameters can also be passed directly to the Execute method instead of adding Parameter objects to the Parameters collection.
Note: If the data type of a parameter is incorrect a "Too few parameters" error will occur.
Public Sub Example()
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim CM As Object 'ADODB.Command
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim PM As Object 'ADODB.Parameter
Dim UserInput As Long
Dim FilePath As String
UserInput = Excel.Application.InputBox("Enter Number:", Type:=1)
FilePath = "C:\ExampleData.xlsx"
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = _
"Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & FilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
CN.Open
Set CM = CreateObject("ADODB.Command")
Set CM.ActiveConnection = CN
CM.CommandType = 1 'adCmdText
CM.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] WHERE Header1 = [Param1]"
'CM.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] WHERE Header1 = ?" 'Also works
CM.Prepared = True
Set PM = CM.CreateParameter("Param1", 3) 'adInteger
PM.Value = UserInput
CM.Parameters.Append PM
Set RS = CM.Execute
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
RS.Close
CN.Close
End SubPublic Sub Example()
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim CM As Object 'ADODB.Command
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim PM As Object 'ADODB.Parameter
Dim UserInput As Long
Dim FilePath As String
UserInput = Excel.Application.InputBox("Enter Number:", Type:=1)
FilePath = "C:\ExampleData.xlsx"
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = _
"Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & FilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 12.0 Xml;HDR=YES"";"
CN.Open
Set CM = CreateObject("ADODB.Command")
Set CM.ActiveConnection = CN
CM.CommandType = 1 'adCmdText
CM.CommandText = "SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$] WHERE Header1 = ?"
CM.Prepared = True
Set RS = CM.Execute(Parameters:=Array(UserInput))
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
RS.Close
CN.Close
End Sub| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| ActiveConnection | The Connection object associate with the Command object. |
| CommandStream | The input stream for the Command object. Mutually exclusive with the CommandText property. |
| CommandText | The text representing the command. Mutually exclusive with the CommandStream property. |
| CommandTimeout | Determines how long in seconds a command will attempt to execute before stopping and returning an error. Default is 30 seconds. |
| CommandType | The command type as a member of the CommandTypeEnum. |
| Dialect | The dialect of the CommandText or CommandStream property. The dialect defines the syntax and rules the provider uses to parse the string or stream. |
| Name | The name of the Command object. |
| NamedParameters | Determines whether or not parameters names should be passed to the provider. |
| Parameters | Contains all Parameter objects for the Command object. |
| Prepared | Determined whether the command is prepared or not. |
| Properties | Contains all Property objects for the Command object. |
| State | Indicates the state of the object as a member of the ObjectStateEnum. Can be a combination of enum members. |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Cancel | Cancels the execution of a pending asynchronous method call. |
| CreateParameter | Creates a new Parameter object. |
| Execute | Executes the query, SQL statement, or stored procedure specified in the CommandText or CommandStream property of the Command object. |
SQL Databases
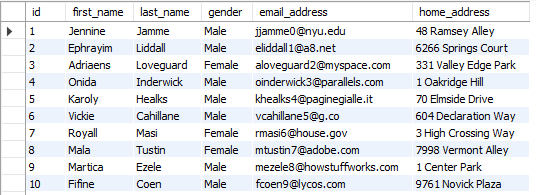
There are various SQL databases including SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. To follow along, download and install the RDBMS of choice and create a test database with a table of sample data. Mockaroo.com was used to generate the sample data for these examples. For these examples, ODBC is being used for each database. Installing the RDBMS should install the necessary ODBC driver(s) but if not be sure to download and install those as well. Add the driver(s) to the DSN using the ODBC Data Source Administrator tool. Find the appropriate connection string for the database you need to connect to and use the classes in the ADODB library to connect to the database and run queries.
SQL Server
To connect to SQL Server using ODBC, it may be necessary to download the ODBC Driver for SQL Server. Add the driver to the DSN. Find the connection corresponding to the driver being used. In this example, a trusted connection is used on the local machine so there is no need for a username and password but these will likely need to be provided in the connection string in a production environment.
Public Sub QuerySQLServerDatabase()
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim Server As String
Dim DBName As String
Dim ConnStr As String
On Error GoTo SafeExit
Server = "localhost"
DBName = "test_database"
'Build connection string
ConnStr = "Driver={ODBC Driver 17 for SQL Server}" _
& ";Server=" & Server _
& ";Database=" & DBName _
& ";Trusted_Connection=yes;"
'Connect to database
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = ConnStr
CN.Open
'Execute query
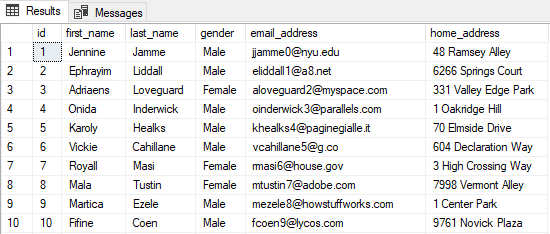
Set RS = CN.Execute("SELECT * FROM person_data")
'Copy results of query to Worksheet
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connection and recordset
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End SubMySQL
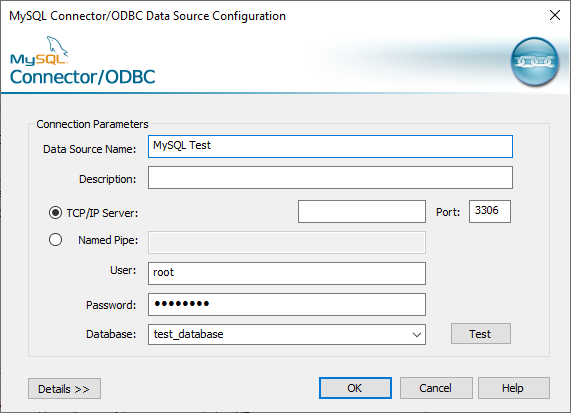
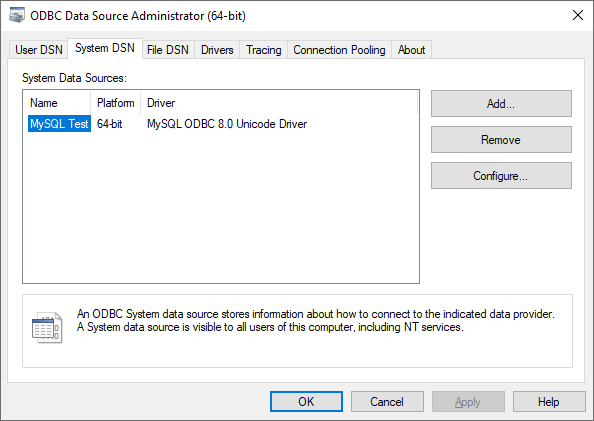
To connect to a MySQL database first add the ODBC driver to the System DSN. Here, the MySQL ODBC 8.0 Unicode Driver is used. Find the connection string corresponding to the driver and if necessary update the version number in the connection string.
Public Sub QueryMySQLDatabase()
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim Server As String
Dim DBName As String
Dim UserID As String
Dim PWord As String
Dim Connstr As String
On Error GoTo SafeExit
Server = "localhost"
DBName = "test_database"
'Get User ID
UserID = InputBox("Enter User ID:")
'***When getting password in a real environment use a more secure technique
PWord = InputBox("Enter Password:")
'Build connection string
Connstr = "Driver={MySQL ODBC 8.0 UNICODE Driver}" _
& ";Server=" & Server _
& ";Database=" & DBName _
& ";User=" & UserID _
& ";Password=" & PWord
'Connection to database
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = Connstr
CN.Open
'Execute query
Set RS = CN.Execute("SELECT * FROM person_data")
'Copy results of query to Worksheet
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connection and recordset
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End SubPostgreSQL
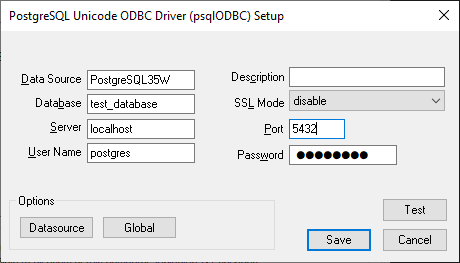
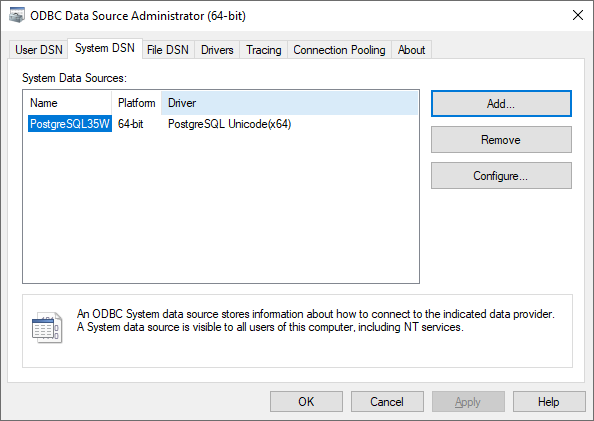
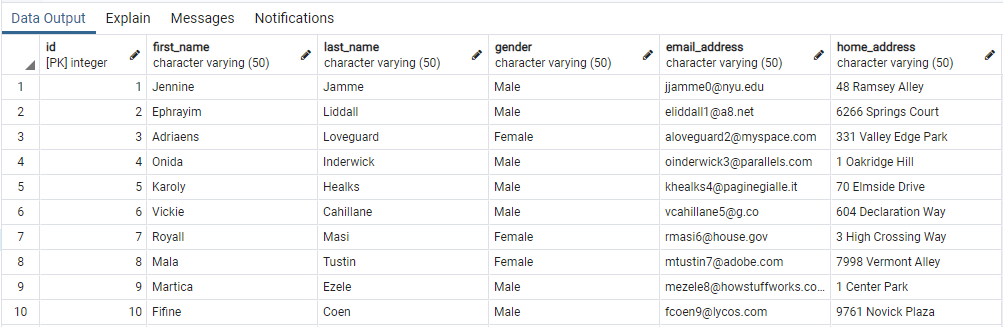
To connect to a PostgreSQL database first install the Postgres ODBC Driver and add the driver to the system DSN. Port 5432 is the default port for Postgres. Find the connection string corresponding to the driver.
Public Sub QueryPostgreSQLDatabase()
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim Server As String
Dim Port As String
Dim DBName As String
Dim UserID As String
Dim PWord As String
Dim ConnStr As String
On Error GoTo SafeExit
Server = "localhost"
Port = "5432"
DBName = "test_database"
'Get User ID
UserID = InputBox("Enter User ID:")
'***When getting password in a real environment use a more secure technique
PWord = InputBox("Enter Password:")
'Build connection string
ConnStr = "Driver={PostgreSQL UNICODE}" _
& ";Server=" & Server _
& ";Port=" & Port _
& ";Database=" & DBName _
& ";Uid=" & UserID _
& ";Pwd=" & PWord & ";"
'Connection to database
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = ConnStr
CN.Open
'Execute query
Set RS = CN.Execute("SELECT * FROM person_data")
'Copy results of query to Worksheet
Range("A1").CopyFromRecordset RS
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connection and recordset
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End SubAccess Databases
To connect to Access files, use the ODBC driver connection string for Access. These examples provide functions for retrieving data from an Access database table and storing it in an array, and for retrieving the names of all tables in a database.
Public Function GetAccessDatabaseTableData(SourceFilePath As String, _
TableName As String) As Variant()
'''Read all from Access database table into 2D Variant array
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim CS As String
Dim i As Long
Dim j As Long
Dim Arr() As Variant
On Error GoTo SafeExit
'Validate Access file exists
If Dir(SourceFilePath) = "" Then
Err.Raise 53
End If
'Build connection string
CS = "Driver={Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb)};" & _
"Dbq=" & SourceFilePath & ";"
'Open connection to Access database
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = CS
CN.Open
'Execute SQL query
Set RS = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
RS.Open "SELECT * FROM " & TableName, CN, 3 'adOpenStatic
'Dimension Array
ReDim Arr(1 To RS.RecordCount + 1, 1 To RS.Fields.Count) As Variant
'Get table headers
For i = 1 To RS.Fields.Count
Arr(1, i) = RS.Fields(i - 1).Name
Next i
'Get data
RS.MoveFirst
For i = 1 To RS.RecordCount
For j = 1 To RS.Fields.Count
Arr(i + 1, j) = RS.Fields(j - 1).Value
Next j
RS.MoveNext
Next i
'Return Array
GetAccessDatabaseTableData = Arr
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connections and cleanup
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End FunctionPublic Function GetAccessDatabaseTableNames(SourceFilePath As String) As Collection
'''Get collection of all table names from Access database
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim CS As String
Dim Arr() As String
On Error GoTo SafeExit
'Validate Access file exists
If Dir(SourceFilePath) = "" Then
Err.Raise 53
End If
Set GetAccessDatabaseTableNames = New Collection
'Build connection string
CS = "Driver={Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb)};" & _
"Dbq=" & SourceFilePath & ";"
'Open connection to Access database
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
CN.ConnectionString = CS
CN.Open
'Get table names
Set RS = CN.OpenSchema(20) 'adSchemaTables
Do While Not RS.EOF
GetAccessDatabaseTableNames.Add RS.Fields("table_name").Value
RS.MoveNext
Loop
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connections and cleanup
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End FunctionExcel Files
To connect to Excel files, use one of the OLEDB connection strings for Excel. These examples provide functions for retrieving data from an Excel Worksheet and storing it in an array, and for retrieving the names of all Worksheets in a Workbook.
Public Function GetExcelData(SourceFilePath As String, _
SourceSheetName As String) As Variant()
'''Reads all data from a spreadsheet into a 2D Variant array using ADO
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim ExcelType As String
Dim QueryString As String
Dim CS As String
Dim i As Long
Dim j As Long
Dim Arr() As Variant
On Error GoTo SafeExit
'Validate Excel file exists
If Dir(SourceFilePath) = "" Then
Err.Raise 53
End If
'Set Excel type string for connection string
Select Case Right$(SourceFilePath, Len(SourceFilePath) - InStrRev(SourceFilePath, "."))
Case "xlsx": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0 Xml"
Case "xlsb": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0"
Case "xlsm": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0 Macro"
Case "xls": ExcelType = "Excel 8.0"
Case Else: Err.Raise 321 'Invalid file format
End Select
'Build connection string
CS = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & SourceFilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""" & ExcelType & ";HDR=YES"";"
'Open connection to Excel file
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.connection")
CN.ConnectionString = CS
CN.Open
'Execute SQL Query
QueryString = "SELECT * FROM [" & SourceSheetName & "$]"
Set RS = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
RS.Open Source:=QueryString, ActiveConnection:=CN, CursorType:=3 'adOpenStatic
'Dimension Array
ReDim Arr(1 To RS.RecordCount + 1, 1 To RS.Fields.Count) As Variant
'Get headers
For i = 1 To RS.Fields.Count
Arr(1, i) = RS.Fields(i - 1).Name
Next i
'Get data
RS.MoveFirst
For i = 1 To RS.RecordCount
For j = 1 To RS.Fields.Count
Arr(i + 1, j) = RS.Fields(j - 1).Value
Next j
RS.MoveNext
Next i
'Return Array
GetExcelData = Arr
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connection and cleanup
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End FunctionPublic Function GetExcelSheetNames(SourceFilePath As String) As Collection
'''Get Collection of all sheet names in a Workbook using ADO
Dim CN As Object 'ADODB.Connection
Dim RS As Object 'ADODB.Recordset
Dim ExcelType As String
Dim CS As String
Set GetExcelSheetNames = New Collection
On Error GoTo SafeExit
'Validate Excel file exists
If Dir(SourceFilePath) = "" Then
Err.Raise 53
End If
'Set Excel file type for connection string
Select Case Right$(SourceFilePath, Len(SourceFilePath) - InStrRev(SourceFilePath, "."))
Case "xlsx": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0 Xml"
Case "xlsb": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0"
Case "xlsm": ExcelType = "Excel 12.0 Macro"
Case "xls": ExcelType = "Excel 8.0"
Case Else: Err.Raise 321 'Invalid file format
End Select
'Build connection string
CS = "Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0" _
& ";Data Source=" & SourceFilePath _
& ";Extended Properties=""" & ExcelType & ";HDR=YES"";"
'Open connection to Excel file
Set CN = CreateObject("ADODB.connection")
CN.ConnectionString = CS
CN.Open
'Get sheet names
Set RS = CN.OpenSchema(20) 'adSchemaTables
Do While Not RS.EOF
GetExcelSheetNames.Add RS.Fields("table_name").Value
RS.MoveNext
Loop
On Error GoTo 0
SafeExit:
'Close connection and cleanup
If Not RS Is Nothing Then
If Not RS.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
RS.Close
End If
End If
If Not CN Is Nothing Then
If Not CN.State = 0 Then 'if adStateClosed
CN.Close
End If
End If
Set RS = Nothing
Set CN = Nothing
If Err.Number <> 0 Then
Err.Raise Err.Number
End If
End Function