VBA Interfaces
An interface provides a template that a class can implement. The implementing class is required to provide definitions for each method and property of the interface. Interfaces are used to implement polymorphism. When a class implements an interface there is a guarantee that a client program can call a particular method or access a particular property because their implementation is required by the interface. Thus, different classes can implement the same interface and client programs can access the same methods and properties of object instances regardless of which class type the object has.
Implementing Interfaces
Interfaces are implemented in VBA by using the Implements statement in a Class Module. To add implementations of interface members for the implementing class use the object box and procedure box drop-downs in the class module's code window to insert the members.
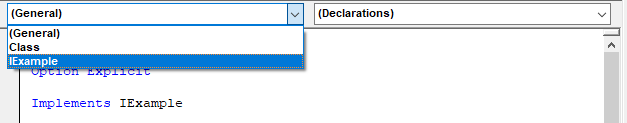
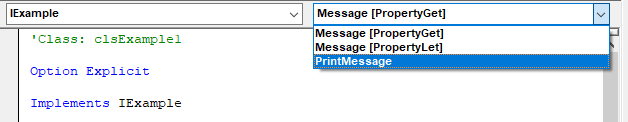
The example below has two classes clsExample1 and clsExample2 that both implement the IExample interface. An array of type IExample is created which can hold instances of any classes that implement IExample. Polymorphism is demonstrated when PrintMessage is called on two separate classes implementing the same interface.
'Standard Module: Module1
Option Explicit
Public Sub Example()
Dim E1 As IExample
Set E1 = New clsExample1
E1.Message = "Hello, World!"
Dim E2 As IExample
Set E2 = New clsExample2
E2.Message = "Hello, World!"
Dim ExampleArr(0 To 1) As IExample
Set ExampleArr(0) = E1
Set ExampleArr(1) = E2
Dim i As Long
For i = LBound(ExampleArr) To UBound(ExampleArr)
ExampleArr(i).PrintMessage
Next i
End Sub'Class: IExample
Option Explicit
Private pMessage As String
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Debug.Print "IExample Initialized"
End Sub
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
Debug.Print "IExample Terminated"
End Sub
Public Property Let Message(RHS As Variant)
pMessage = RHS
End Property
Public Property Get Message() As Variant
Message = pMessage
End Property
Public Sub PrintMessage()
Debug.Print "Message from IExample: " & pMessage
End Sub'Class: clsExample1
Option Explicit
Implements IExample
Private pMessage As String
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Debug.Print "clsExample1 Initialized"
End Sub
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
Debug.Print "clsExample1 Terminated"
End Sub
Private Property Get IExample_Message() As Variant
IExample_Message = pMessage
End Property
Private Property Let IExample_Message(RHS As Variant)
pMessage = RHS
End Property
Private Sub IExample_PrintMessage()
Debug.Print "Message from clsExample1: " & pMessage
End Sub'Class: clsExample2
Option Explicit
Implements IExample
Private pMessage As String
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Debug.Print "clsExample2 Initialized"
End Sub
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
Debug.Print "clsExample2 Terminated"
End Sub
Private Property Get IExample_Message() As Variant
IExample_Message = pMessage
End Property
Private Property Let IExample_Message(RHS As Variant)
pMessage = RHS
End Property
Private Sub IExample_PrintMessage()
Debug.Print "Message from clsExample2: " & pMessage
End Sub